GPU Benchmarks and Hierarchy 2023
As technology evolves, the performance of graphics processing units (GPUs) becomes increasingly crucial in various computing tasks. Tom's Hardware provides an exhaustive benchmarking of both current and previous generation GPUs, ranking them based on performance. This GPU benchmarks hierarchy is essential for understanding the capabilities of graphics cards in different contexts, from gaming and AI workloads like Stable Diffusion to professional video editing.

The Role of GPUs in Computing Performance
In the realm of computing, especially gaming and AI, the graphics card often plays a pivotal role in determining overall performance. While the best CPUs for gaming are important, they usually take a secondary role compared to the capabilities of the GPU. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for anyone looking to optimize their computer for specific tasks.
Also check Windows Mixed Reality Deprecation
Methodology: Benchmarking Ray-Tracing Capable GPUs
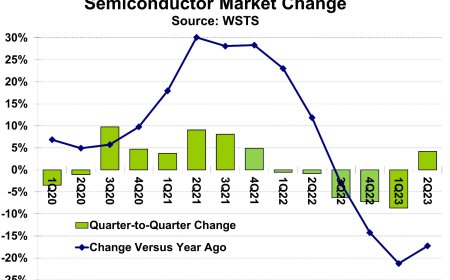
Recently, Tom's Hardware has retested all ray-tracing capable GPUs using a revamped test suite, transitioning from a Core i9-12900K to a more powerful Core i9-13900K. This change reflects an effort to provide more accurate and up-to-date benchmarking results. While recent reviews utilize the updated test PC, the hierarchy still includes data from the older PC setup for a comprehensive view.
The Latest in GPU Hierarchy: Intel's Arc A580
A significant update to the GPU hierarchy is the addition of Intel's Arc A580. This newcomer is a bit slower than the A750 and competes closely with the RX 6600, albeit with higher power consumption. The entry of Intel's Arc A580 marks an interesting shift in the GPU landscape.
Traditional Rendering vs. Ray Tracing GPU Benchmarks
The article presents two distinct GPU hierarchies: one for traditional rendering (rasterization) and another for ray tracing benchmarks. Ray tracing, requiring specific GPU capabilities, limits the field to AMD's RX 7000/6000-series, Intel's Arc, and Nvidia's RTX cards. It's important to note that the results exclude the use of DLSS, FSR, or XeSS enhancements.
Nvidia’s RTX 40-Series: Ada Lovelace Architecture
Nvidia's latest generation RTX 40-series is powered by the Ada Lovelace architecture. This series introduces new features like DLSS 3 Frame Generation. Additionally, Nvidia plans to release DLSS 3.5 Ray Reconstruction for all RTX cards, further enhancing their performance capabilities.
AMD’s RX 7000-Series: RDNA 3 Architecture
AMD's response to the GPU race comes in the form of its RDNA 3 architecture, powering the RX 7000-series. This series boasts five desktop cards, each designed to offer robust performance and compete with Nvidia's offerings.
Intel’s Entry with Arc Alchemist Architecture
Intel's foray into the dedicated GPU market with its Arc Alchemist architecture introduces a third competitor. While it's more aligned with previous generation midrange offerings, Intel's presence is a significant addition to the GPU landscape.
Benchmark Suite 2020–2021: Legacy Performance Data
The article also provides a look at the 2020–2021 benchmark suite, which includes performance data for previous generation GPUs. These tests, conducted on a Core i9-9900K testbed, offer valuable insights into the evolution of GPU performance over recent years, though they are no longer actively updated.
Legacy GPU Hierarchy: Theoretical Performance Comparison
For reference, the article includes a legacy GPU hierarchy that sorts graphics cards by their theoretical performance. This section doesn't include benchmarks but serves as a useful tool for comparing older GPUs.
Benchmark Results: Gaming Performance at 1080p
The core of the article lies in the detailed benchmark results. GPUs are ranked based on their gaming performance, with tests conducted at 1080p "ultra" settings for the main suite and 1080p "medium" for the DXR suite. This focus allows for a clear comparison of GPUs based solely on performance in gaming scenarios.
Excluding Factors: Price, Power Consumption, and Efficiency
It's important to note that the rankings in the article do not consider factors like price, power consumption, overall efficiency, and additional features. The focus is strictly on raw performance as demonstrated in the gaming benchmarks.