Nvidia's RTX 4090D Dragon GPU
Nvidia, a prominent player in the world of graphics processing units (GPUs), has introduced a China-specific GPU, the GeForce RTX 4090D Dragon. This exclusive GPU has been developed to align with the United States' export regulations, ensuring compliance with geopolitical requirements. In this article, we delve into the details of the RTX 4090D Dragon, exploring its key specifications, pricing, and the reasons behind its creation.
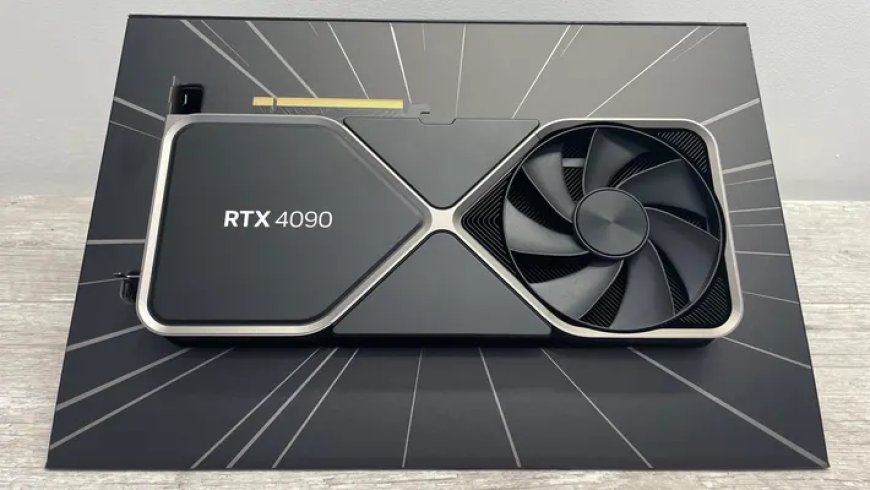

Specifications of the RTX 4090D Dragon
The RTX 4090D Dragon boasts a formidable set of specifications. It is equipped with 14,592 CUDA cores, providing substantial processing power. This GPU features 24GB of GDDR6X memory, ensuring ample capacity for demanding tasks. The memory interface comprises a 384-bit wide bus, facilitating rapid data transfer. In terms of power consumption, the RTX 4090D Dragon has a rating of 425W.
Also check Corsair Xeneon Flex 45" Review: A Unique Bendable OLED Experience
Pricing Parity with the RTX 4090
Nvidia has maintained pricing parity between the RTX 4090D Dragon and its flagship GPU, the RTX 4090. Both GPUs are priced at ¥12,999 (approximately $1,828). This pricing strategy ensures that Chinese consumers have access to a high-performance Nvidia GPU without incurring additional costs due to geopolitical considerations.
Comparing the RTX 4090D Dragon to the RTX 4090
While the RTX 4090D Dragon aligns with the RTX 4090 in terms of pricing and several core specifications, there are notable differences between the two GPUs. The most significant distinctions lie in the number of CUDA cores and power consumption.
-
CUDA Cores: The RTX 4090D Dragon features 14,592 CUDA cores, marking a 12.8% reduction compared to the RTX 4090's 16,384 CUDA cores. This reduction is primarily attributed to differences in the Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs), with the RTX 4090D Dragon housing 114 SMs while the RTX 4090 has 128 SMs.
-
Power Consumption: The RTX 4090D Dragon exhibits a slightly lower power draw, rated at 425W, which represents a modest 5.9% reduction from the RTX 4090's 450W power consumption. This reduction contributes to improved energy efficiency while maintaining high-performance capabilities.
The Geopolitical Context: Export Regulations and Total Processing Power (TPP)
The introduction of the RTX 4090D Dragon is a direct response to the evolving geopolitical landscape and export regulations imposed by the United States. These regulations have compelled Nvidia to discontinue the sale of the standard RTX 4090 and other AI/HPC-focused GPUs to the Chinese market.
Under the new export rules, chip manufacturers like Nvidia are restricted from shipping semiconductor processors that exceed specific performance metrics established by the United States. One critical metric utilized is known as Total Processing Power (TPP). TPP is calculated based on the maximum compute performance for a given bit-length, measured in TFLOPs or TOPS, multiplied by the number of bits.
The U.S. export regulations set a maximum TPP threshold of 4,800. Unfortunately, the RTX 4090 exceeded this threshold, boasting a TPP of 5,286, which led to its inclusion on the list of prohibited exports.
Conclusion: The RTX 4090D Dragon's Role in Chinese Market Access
In conclusion, Nvidia's launch of the GeForce RTX 4090D Dragon addresses the challenges posed by export regulations and geopolitical considerations, ensuring continued access to high-performance GPUs for the Chinese market. While it offers slightly reduced CUDA cores and improved energy efficiency compared to the RTX 4090, the RTX 4090D Dragon maintains pricing parity, making it an attractive option for Chinese consumers seeking powerful graphics solutions. This GPU exemplifies the dynamic nature of the tech industry, where innovation and adaptability are key to navigating complex global landscapes.