Raspberry Pi Zero 2W single board microcomputer
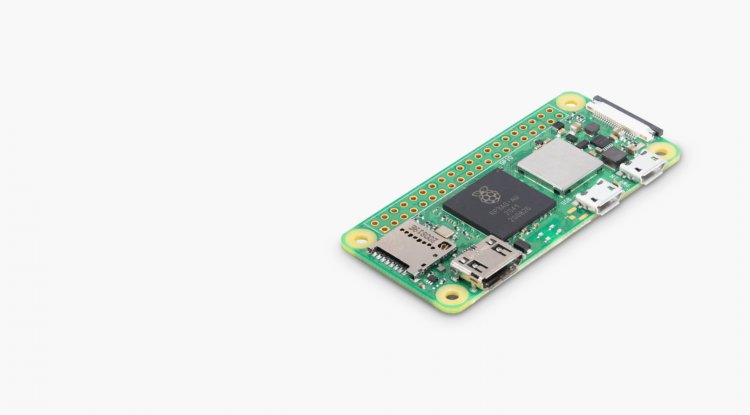

The Raspberry Pi Foundation in the United Kingdom creates single-board microcomputers to enhance computer science education in schools and hobby communities. They are available in a variety of sizes, performance levels, and port counts. The larger "B" series model, which is now in version 4, has the most powerful processor and a plethora of port options, including two micro HDMI connectors for attaching displays. There is also a Raspberry Pi 400 model incorporated within the keyboard. The Raspberry Pi Pico development board, which costs $ 4, is the smallest and cheapest member of the Raspberry product family. Pico has the proportions of a traditional 40-pin chip, no video output, and is intended primarily as a control unit for various amateur builds. Although it is only slightly larger than the Pico, the Raspberry Pi Zero board is 65 x 31 mm. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lKS2ElWQizA
The Zero, like the bigger B-Series machines, runs a variety of Linux-based operating systems. Using the Raspberry Pi Imager application, the operating system is installed on a micro SD card. By default, Raspberry OS is recommended. The Raspberry Pi Zero 2W microcomputer board costs around 16 dollars and most online stores enable you to order only one piece at a time. The cause is not the chip crisis, as Raspberry microcontrollers are not used in automobiles, but rather the cost. Because this board is primarily meant for education, the pricing is calculated almost without a margin. As a result, several companies might include this board in their goods; nevertheless, the board was not intended for such application.
When compared to its single-core predecessor, the new Raspberry Pi Zero board with a 2W characteristic and a dual-core processor has 40% higher single-fiber and five times higher multi-fiber performance. The letter "W" in the label indicates that the board enables WiFi communication. The Raspberry Pi Zero 2 W fits into most existing Raspberry Pi Zero boxes due to its same design and identically spaced connectors. A micro USB connector is also utilized for the power supply, but because the processor is more powerful, a more powerful power supply capable of supplying 2.5A at 5V is necessary.
The RPi Zero 2 W features the same 40-pin GPIO connector as other Raspberry Pi computers, but it does not come with any pins. The header with pins may be too large for some smaller structures, and due to the smallest available dimensions, it is often more advantageous to solder the wires directly to the board.
The Broadcom BCM2710 A1 SoC (System on Chip) at the heart of the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W contains four Cortex-A53 cores clocked at 1 GHz. It is built in a common casing with 512 MB LPDDR2 SDRAM memory and is manufactured in 40 nm technology. The case of such a kit is labeled Raspberry Pi RP3A0. Interestingly, the Raspberry Pi 3 uses the same SoC BCM2710A1 family, but it has CPU cores clocked at 1.2 GHz and 1 GB of RAM.
In other words, you shouldn't expect the same performance from the Raspberry Pi Zero as you would from the Raspberry Pi 3, but for less demanding applications like the Thonny development environment for the Python programming language, basic web browsing, or simpler games, the performance and memory capacity of the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W are adequate. Furthermore, performance is enough for simple artificial intelligence applications such as image recognition using Tensorflow Lite, voice, machine learning, and so on. RAM capacity is frequently the bottleneck. It should be noted that the 512 MB installed capacity is shared with the graphics core, leaving the operating system with around 450 MB available.
If you wish to use more power permanently, or if you want to overclock the processor, we propose installing a heatsink or using a fan to boost cooling efficiency.
After installing the operating system, you can increase the clock speed by adding lines to the /boot/config.txt file, for example.
over_voltage = 4
arm_freq = 1200
core_freq = 500
The sudo nano /boot/config.txt command opens the /boot/config.txt file in a terminal application. This allows you to raise the processor clock speed to 1.2 GHz (1200 MHz), or by 30%, as well as the VideoCore IV 500 MHz graphics core, resulting in improved graphics performance. Of course, appropriate cooling of the chip is required, which can be accomplished by bonding an aluminum finned heatsink.
The Broadcom VideoCore IV graphics processor supports OpenGL ES 1.1, 2.0, as well as H.264 and MPEG-4 video decoding (1080p30). The highest resolution is full HD, which is 1920 x 1080 pixels, or 1080p. To connect the monitor, a tiny HDMI connector is available. To connect the RPi Zero to the monitor, you'll need a mini HDMI-to-HDMI converter or a cable with a mini full-size HDMI connector on one end and a regular full-size HDMI connector on the other. Alternatively, you can use a composite video connection, with the signal available at the test point via the RCA (Cinch) connector.
You can use this way, for example, to connect to older TVs that lack an HDMI input. You're probably wondering why the Raspberry Pi is linked to an old TV. One of the reasons is that there are various preconfigured vintage video game operating system variations, such as Retro Pie, available for the Raspberry Pi Zero. Retro games, on the other hand, have the proper atmosphere on a retro TV. For miniature projects, the display on a suitable LCD display connected via the SPI interface can be used.
On the PCB, there are two micro USB ports. One is powered, while the other utilizes the USB 2.0 standard for connecting external devices like keyboards and mice. To connect devices with a USB-A connector, a USB OTG (On-The-Go) reduction must be used. For example, you can use a kit that employs a common USB radio dongle, an active USB hub, or a keyboard with an integrated touchpad to overcome the difficulty of attaching a keyboard and mouse to a single port.
Because the GPIO connectors and the CSI connector for connecting the camera are the same as on other Raspberry boards, projects made for prior boards can be readily moved to a newer, more powerful board. Bluetooth 4.2, including Bluetooth Low Energy, is supported by the Raspberry Pi Zero 2W. (BLE). When connecting to WiFi, keep in mind that the printed circuit board contains a small antenna, thus the connection works best if the board is close to the WiFi router.
To familiarize yourself with the development board's capabilities, we recommend modules from Grove kits built for quick prototyping.
Sensors, motors, servo motors, relays, displays, LEDs, rotary encoders, and other hardware components are included in the kits. Each module in the kit is meant to perform a single function, such as monitoring temperature, humidity, measuring distance using ultrasound, presenting data on the screen, and so on. Simply plug in the Base Shield motherboard and you're ready to put your ideas to the test. The Grove Base hat expansion board for the Raspberry Pi Zero is required for the Raspberry Pi Zero development board. The connectors are designed to be inserted correctly only.
All that is required is that you connect the analog interface modules to the analog connectors, the modules that require digital inputs to the digital connectors, and the outputs to the digital connectors. which use the communication bus must be connected to the relevant communication interface socket I2C, UART, and servomotors to the PWM connections. Even if you make an unintentional error, you will not cause any harm; however, the connection will not work for you. Because the Raspberry lacks analog inputs, another STM32 microcontroller on the Grove Base hat supplies a 6-channel 12-bit ADC converter.
Screens, various single-purpose measuring or communication devices, multimedia centers, mini-game consoles with color displays, monitoring cameras, audio converters, measuring devices, or robotic constructions are among the many extension modules available.