How Fiber Optic Cables Work
How Fiber Optic Cables Work Fiber optic cables have revolutionized the way we transmit data, offering high-speed, high-capacity connectivity that has changed the way we live and work. With its advanced technology and innovative design, fiber optic cables are capable of transmitting massive amounts of data over long distances, making them a critical component of modern communication networks. In this article, we'll take a closer look at how fiber optic cables work, exploring their key components, and the science behind their operation.
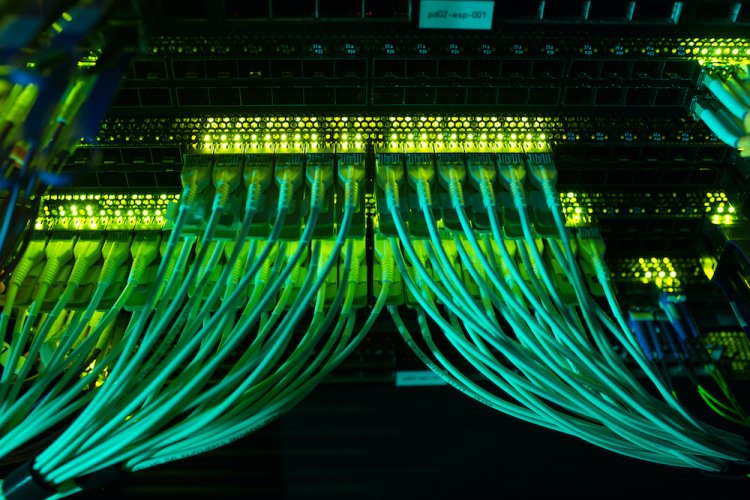

What is a Fiber Optic Cable?
A fiber optic cable is a type of cable that uses light to transmit data. It consists of a thin glass or plastic fiber, surrounded by protective materials, which carries light signals over long distances. Unlike traditional copper cables, which transmit data using electrical signals, fiber optic cables use light to transmit data, which provides a number of key advantages, including faster speeds, higher bandwidth, and greater reliability.
How Does a Fiber Optic Cable Work?
A fiber optic cable works by transmitting light signals along the length of the cable. The light signals are generated by a light source, such as a laser or an LED, and are guided along the cable by a series of reflective surfaces. When the light reaches the end of the cable, it is received by a detector, which converts the light signals back into electrical signals that can be interpreted by a computer or other device.
Key Components of a Fiber Optic Cable
There are several key components of a fiber optic cable, including:
-
Core: The core is the central part of the fiber optic cable, and is made of a thin glass or plastic fiber. It is the part of the cable that carries the light signals.
-
Cladding: The cladding is a layer of material that surrounds the core and helps to keep the light signals contained within the cable. It is typically made of a different material than the core, and is designed to have a lower index of refraction, which helps to keep the light signals reflected back into the core.
-
Buffer Coating: The buffer coating is a layer of material that surrounds the cladding and protects it from damage. It is typically made of a soft, flexible material, such as acrylate or polyurethane, and is designed to provide a layer of insulation around the cladding.
-
Outer Jacket: The outer jacket is a layer of material that surrounds the buffer coating and provides additional protection for the cable. It is typically made of a durable material, such as polyethylene, and is designed to protect the cable from environmental factors, such as moisture, temperature changes, and physical damage.
Also Check You can now buy the world's first USB-C iPhone
Advantages of Fiber Optic Cables
There are several key advantages to using fiber optic cables, including:
-
High-speed connectivity: Fiber optic cables are capable of transmitting massive amounts of data over long distances, providing high-speed connectivity that is ideal for a wide range of applications.
-
High bandwidth: Fiber optic cables offer high bandwidth, making them ideal for applications that require large amounts of data to be transmitted, such as high-definition video and audio.
-
Reliable performance: Fiber optic cables provide reliable performance, even in challenging environments, making them a dependable choice for mission-critical applications.
-
Immunity to electromagnetic interference: Unlike traditional copper cables, fiber optic cables are immune to electromagnetic interference, making them a more reliable choice for sensitive applications.
-
Long distances: Fiber optic cables can transmit data over much longer distances than traditional copper cables, making them a more cost-effective choice for long-haul communication networks.